Dare to Ask
[Grown-ups] never ask questions about what really matters
The Little Prince, Antoine de Saint-Exupéry
We’ve seen businesses failing to ask questions that
beg to be asked:
More Of Uncomfortable Questions
Many More Up Our Sleeve


Find out what questions you’re failing to ask
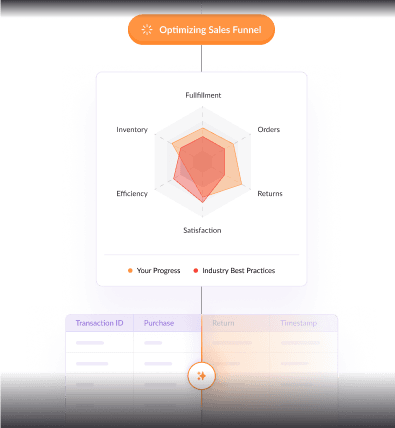
Stemscale’s Enterprise Data Management (EDM) provides the foundational data for the Financial Analytics needed for businesses to derive accurate financial insights that inform strategic decisions. Accurate financial insights, however, require not just data, but data integrity and consistency. The EDM, as we designed it, curates data every step of the way to inform strategic decisions
Peeling Back the Layers
Energize Your Financial Insight
Engage in dynamic scrutiny of your balance sheets, income, and cash flow statements
Employ vigorous ratio analysis to reveal the vitality and earnings power of your business
Harness the forward momentum of trend analysis to chart your company’s fiscal voyage
Elevate Your Investment Game
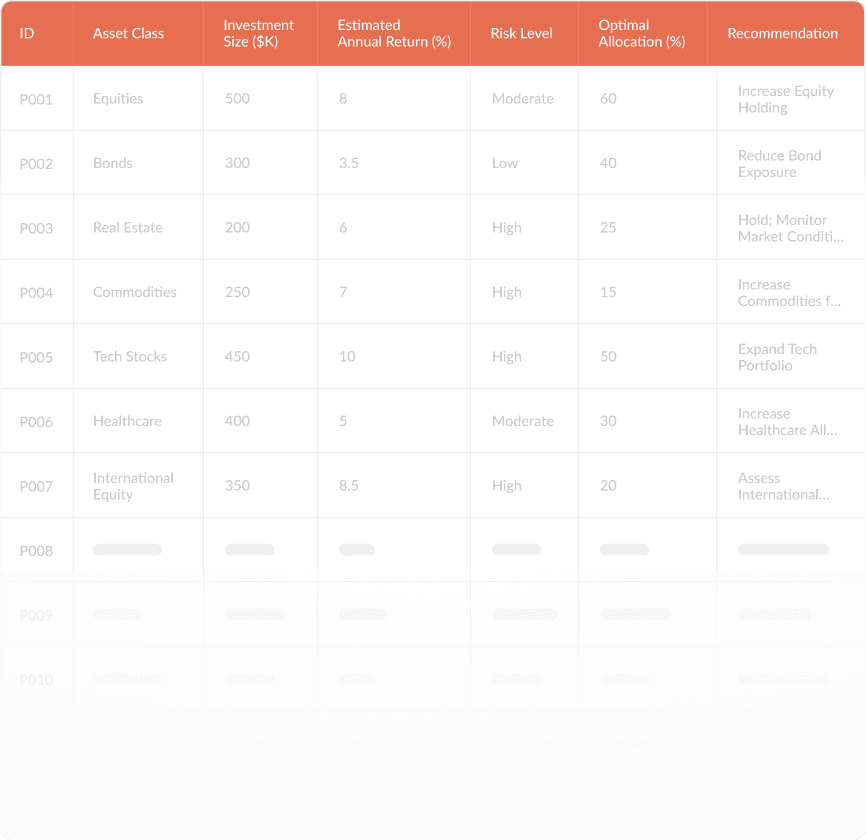
- Do high-powered portfolio analysis and optimization for peak performance
- Navigate the landscape of risk-return profiling for potential investments
- Seize expert asset allocation recommendations to strategically amplify your portfolio’s potential.
Sector-Specific Market Research And Analysis
Do the research and analysis into pulse-quickening economic trends
Explore market sizing and segmentation, unlocking new territories of opportunity grounded in share analysis
Engage in the game of competitor analysis and benchmarking, staying always two steps ahead
Delve into the mind of your consumer with behavior and sentiment analysis.
Our Enterprise Data Management (EDM) helps us ensure that the data used for market research is accurate and up-to-date, facilitating better market understanding and strategic positioning.
Bespoke Financial Modeling
- Let budgeting, forecasting, and financial projections inform your decisions
- Examine opportunity costs of decisions
- Play out the ‘what-ifs’ through scenario and sensitivity analysis
- Conduct attribution analysis to understand performance drivers
- Examine interest rate risks
Corporate Finance
Capital acquisition, leveraging a mix of equity, debt, and hybrid financing solutions tailored to enhance your business’s growth and stability
Achieve accurate asset and business valuations for informed decision-making. Our expert appraisals, including Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis, support investment strategies, financial reporting, and regulatory compliance
Put International Financial Reporting Standards to work (IFRS)
let us help you transition to IFRS & explain how your businesses may benefit from using IFRS apart from making your financial reporting accurate and transparent.
Let IFRS give you a better understanding of where you are
Navigate the complexities of mergers and acquisitions from deal scouting to post-merger integration. Our comprehensive guidance ensures you capitalize on synergies and enhance shareholder value. See industry profiles for detail
Variance Analysis
Bridge the gap between planning and execution in the financial realm. VA could be your vital tool to make informed decisions for future financial planning and strategy
Make projections for revenue and expenses based on historical data, market research, and future expectations
Measure actual performance against the baseline of these projections
Track financial performance on a monthly, quarterly, annual basis to ensure that operations align with the budgeted expectations
Identify positive and negative variances, i.e. favorable & unfavorable deviations from the budget
Categorize variances by their nature and source, such as sales volume variance, pricing variance, cost variance, and efficiency variance
Pinpoint specific areas that are performing differently than expected
Investigate the causes of variances, whether they are due to internal factors (operational inefficiencies) or external factors (market changes, economic conditions) to link actual performance with budgeted figures
Inform management about the aspects of the business that are not aligned with the plan to introduce cost control measures, price adjustments, or strategic shifts
Update forecasts accordingly to make them more accurate for future periods, e.g. adjusting budget expectations for revenues or expenses if variances indicate a trend
Take corrective actions to ensure that business operations are within the boundaries of the financial plan
Get your expenditure distribution right is critical to competitive pricing.
Risk Analysis
Get a fresh perspective free of your potential biases or blind spots, by exploring alternative risk mitigation strategies/suggestions
Assess risks associated with business operations, including process inefficiencies and supply chain disruptions
Assess credit risks, market risks, and liquidity risks to ensure the stability and profitability of the business. Preventing financial distress, including bankruptcy, is seldom appreciated—hypotheticals are hard to believe. Our risk analysis ensures financial distress remains a hypothetical
Examine risks related to strategic decisions, such as market entry, mergers and acquisitions, and competitive positioning, to ensure long-term business growth and sustainability
We add the most value to risk assessment when we focus on risks best seen from the outside, provided we ask you the right questions to get your insider perspective, viz.,
- comfort risks, which happen when company’s leadership grows overly comfortable with the firm’s performance, neglecting enhancements to its products or services.
- counterparty risks, which happen when the other party in a transaction fails to fulfill their obligations.
- liquidity risks, which occur when a business cannot meet its short-term financial obligations due to a lack of cash or easily tradable assets.
- competition risks, which happen when a competitor captures a growing portion of the market for a particular product or service
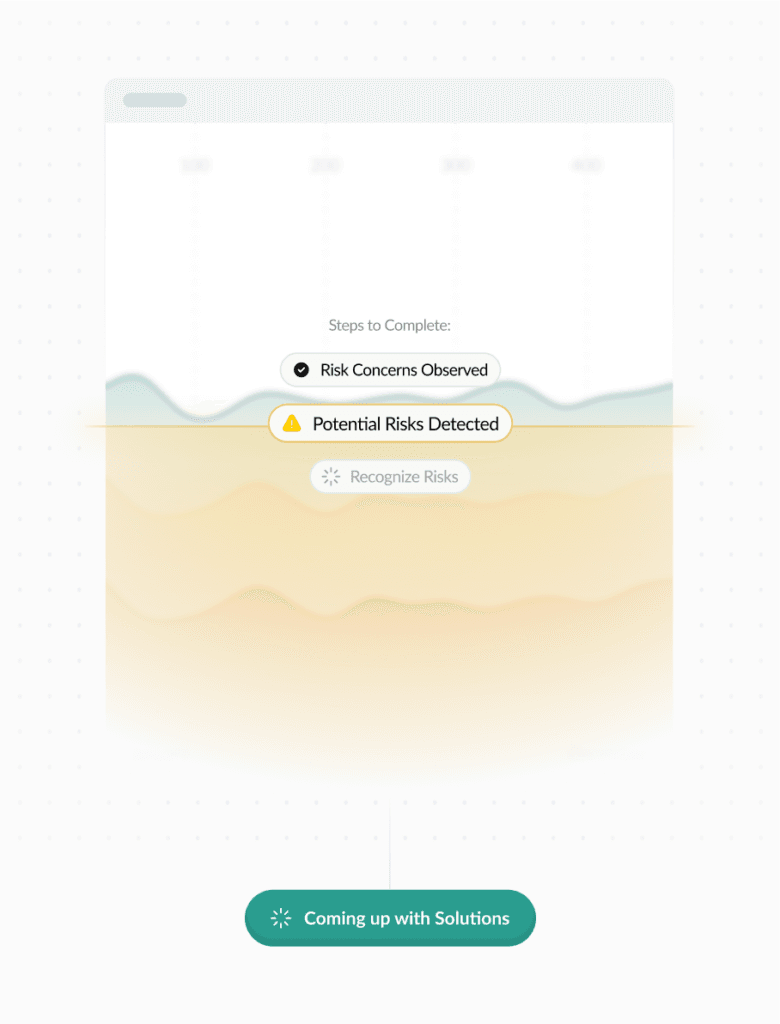
However, some operational risks are often best identified, understood, and managed internally, with or
without help from specialized consultants. Internal stakeholders have a more nuanced understanding of the company’s operations, culture, and internal dynamics, such as employee morale and cultural issues —
internal tensions, dissatisfaction, and conflicts among employees that affect productivity and engagement; unwritten workarounds — informal methods to bypass inefficient formal processes that outsiders might
not detect; the influence of informal leaders and the true power dynamics that affect decision-making.
Rethinking Performance Metrics
We offer a fresh look at selection and use of performance indicators in business through our longer-term lens — a holistic approach that draws on Goodhart’s Law, introduced by Charles Goodhart, a British economist. The Law posits that when a measure becomes a target, it ceases to be a good measure. The law has prompted us to using a variety of metrics and continual reassessment to argue for careful selection and balanced use of performance indicators in business
Goodhart’s Law extends to many areas of life. Most of us have either heard of or met people who, aiming for a certain body fat percentage, adopt extreme measures that neglect their holistic well-being. In our capacity as business consultants, we have seen businesses
prioritize short-termism over long-termism, neglecting their brand relevance and resonance much like individuals neglect their holistic well-being
fail to ask critical questions about the meaning their brand holds and how relevant it is in people’s lives
A metric selected as a performance indicator often leads to unintended consequences. We call these Goodhart pitfalls. You might have come across examples of Goodhart’s Law in action yourself but have not recognized them as such — businesses prioritizing getting their name out there (awareness) over creating meaningful connections (relevance) or deep emotional bonds (resonance) with their customers or other myopic decisions.
Common Goodhart pitfalls we’ve encountered:
Modelling The Impact Of Overcharging
Pricing Pitfalls
We help businesses find their pricing sweet spot, balancing fair value and sustainable growth to avoid the pitfalls of both underpricing and aggressive overcharging — two extremes of the spectrum. The price for the aggressive overcharging could be your brand and customer trust damaged. Underpricing, on the other hand, could lead to missed revenue and stalled growth as competitors outmaneuver price laggards
While deep discounts may be necessary at times, they can disrupt sales during the ‘non-sale’ cycle by increasing customers’ price sensitivity or diminishing the perceived value of products when they’re not on sale
Sales targets become the exclusive focus when sales quotas drive salespeople to oversell products/services to customers who don’t need them. Customers perceive this as deceptive marketing, ultimately leading to their dissatisfaction and potential losses for the business in the medium to long run.
Balancing your sales approach is crucial to avoiding both overselling and the pitfalls of a static pricing strategy
Price gouging eventually “punishes” price gougers. The “punishment” comes from what we call intertemporal adjustment, which happens when consumers opt for cheaper goods or services in Period B because they had to pay more than usual in Period A.
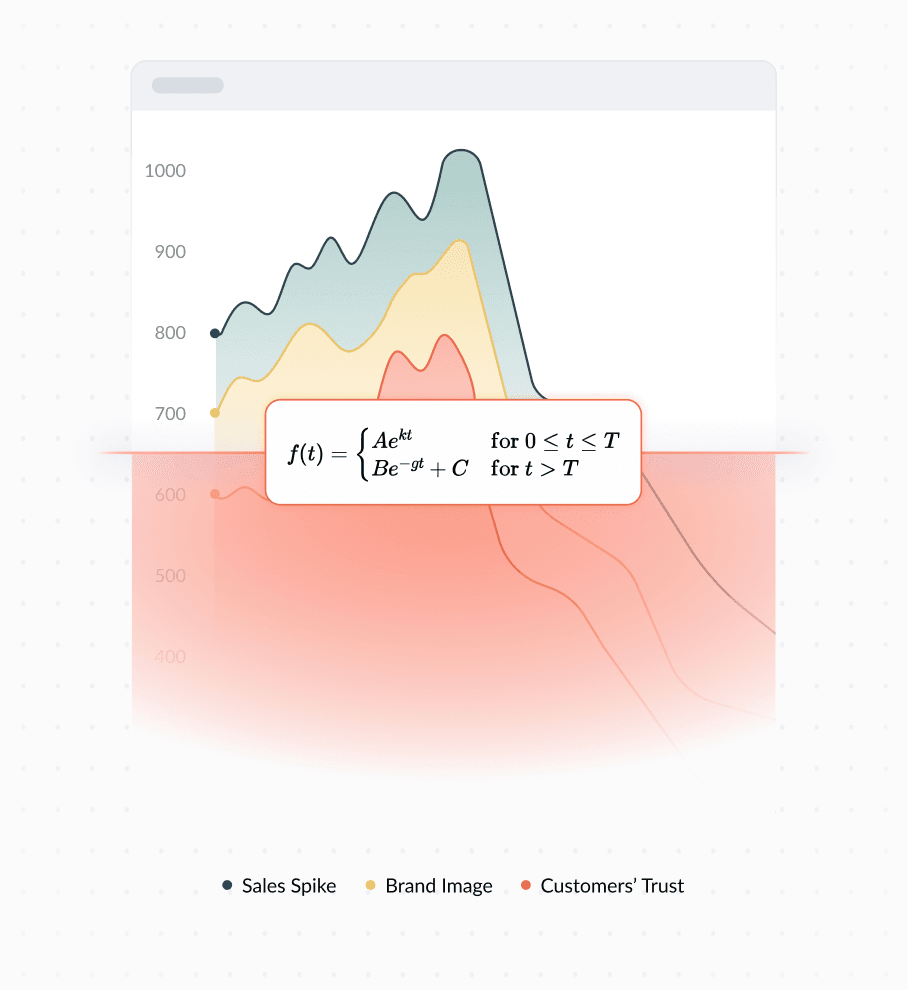
The Impact of Overcharging
Formula Breakdown
This formula captures the exponential growth due to aggressive tactics until time T, after which there is an exponential decline, adjusted by the constant C to fit the context or baseline sales level.
t is the time. The sales change as time progresses
T is the time at which the peak occurs and the sales strategy shifts from growth to decline
A, B, and C are constants in the formula that adjust how the sales volume behaves. A affects the initial sales volume, B and C adjust how the sales decline and settle after the peak
k is the growth rate during the aggressive sales period. A higher k means sales ramp up quickly
g is the rate of decline after the peak. A higher g means sales drop off more rapidly after the peak.
Aekt Here, sales grow exponentially. The term “exponential” means the growth accelerates over time; it starts off slow and then speeds up dramatically. This part of the formula captures how aggressive tactics (like big promotions or ads) can rapidly increase sales.
Be−gt+C After reaching the peak, sales start to decline exponentially. The sales don’t just return to normal but initially drop quite steeply due to possibly market saturation or customer fatigue. Over time, the decline slows down and approaches a baseline level (given by C), which might represent the normal sales level without promotions.
This model shows that while aggressive tactics can create a quick boost in sales, these are not sustainable, and there’s usually a sharp drop-off. Understanding and anticipating this pattern can help in planning better sales strategies and avoiding potential pitfalls of overly aggressive marketing.
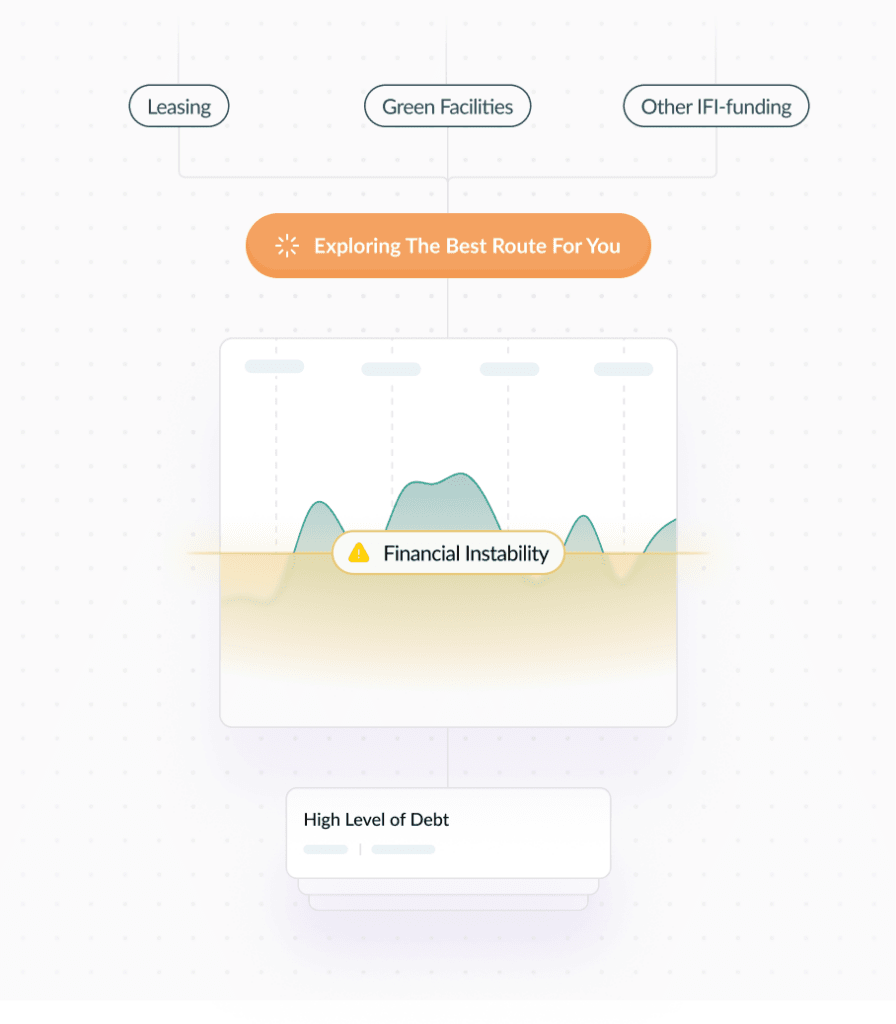
Excessive Debt Financing
Companies taking on high levels of debt to fund expansion or increase shareholder dividends
High interest payments heavily contributing to companies’ financial instability in the medium to long run
Companies failing to explore alternative financing routes: leasing, green and other IFI-funded development facilities
Let us help you understand why you might want to decline an immediate cash influx that seems crucial.
Employee Performance Metrics
Companies set very specific performance metrics for employees, such as answering a certain number of calls or processing a specific amount of emails per hour for customer service representatives
Employees often focus exclusively on meeting these metrics, frequently at the expense of quality service, as they rush through calls or emails without fully addressing customer concerns or needs
Ignoring Sustainability
We’ve seen the focus on short-term profits lead to underinvestment in employee training and development, reducing short-term labor costs
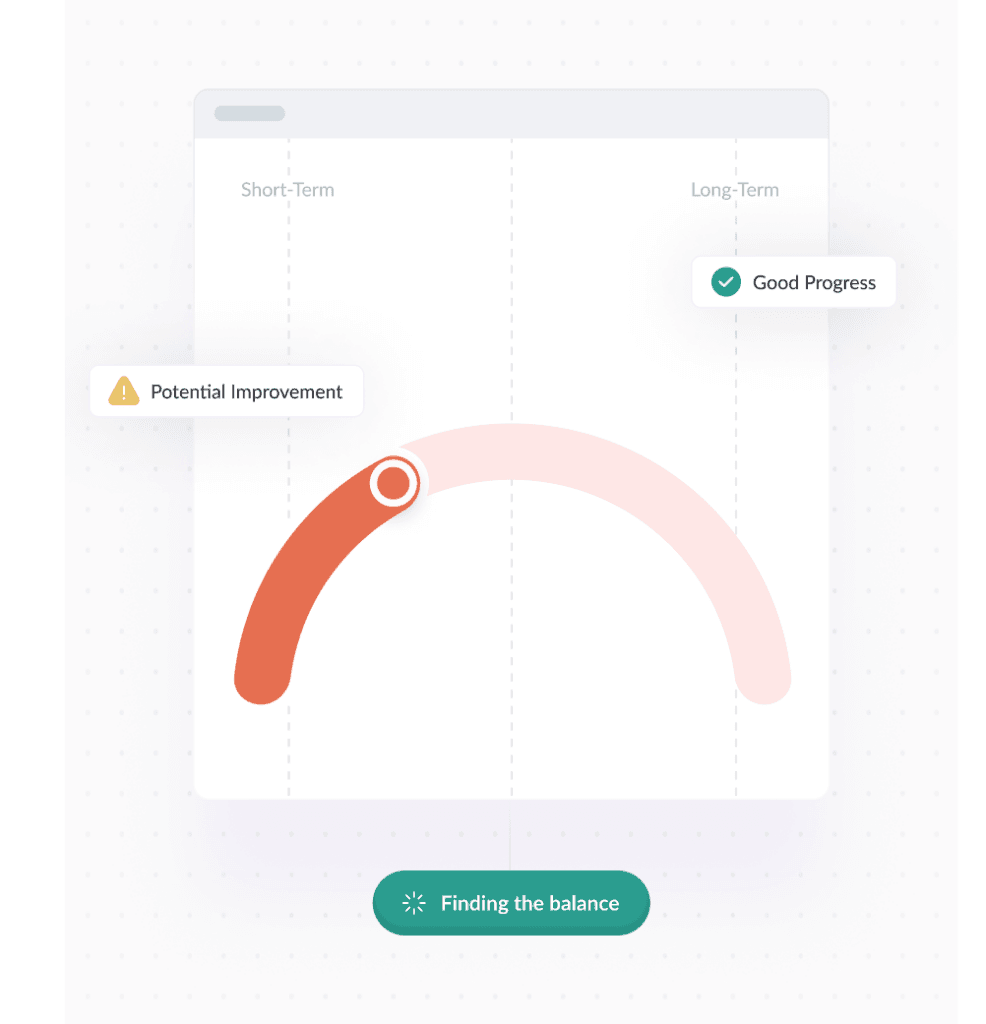
There’s nothing wrong with focusing on the short-term as long as you strike a balance between short-term and long-term objectives to ensure sustained growth, stability, and competitiveness.